ACTINIC KERATOSIS
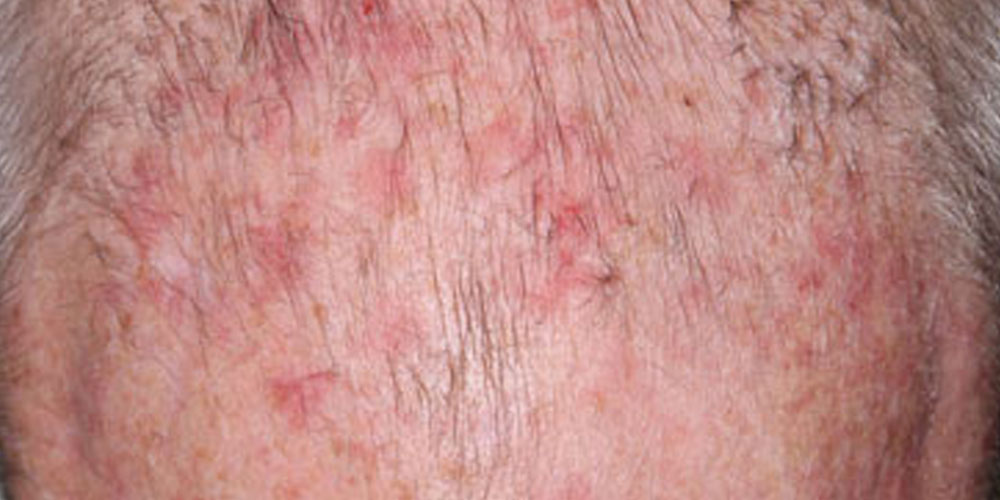

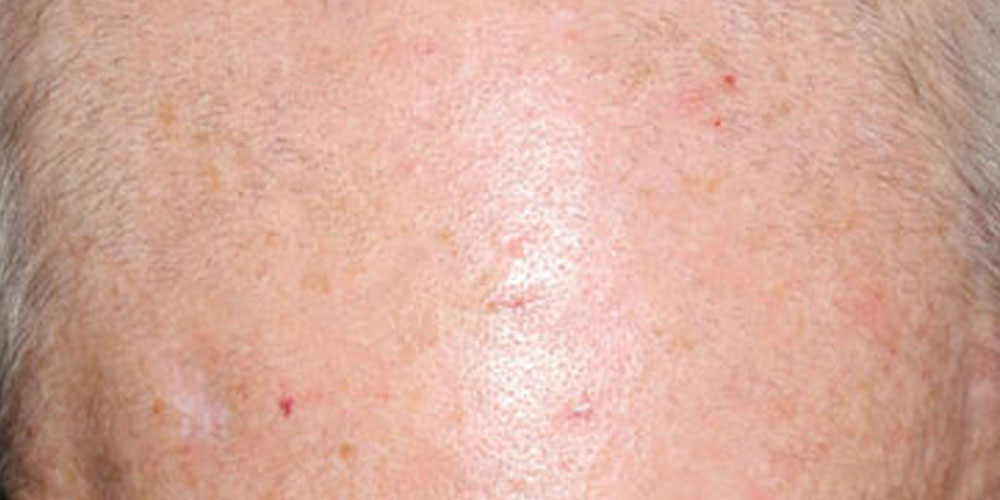
An actinic keratosis (AK) is a rough, scaly patch on your skin that develops from years of exposure to the sun. It’s most commonly found on your face, lips, ears, back of your hands, forearms, scalp or neck. Also known as a solar keratosis, an actinic keratosis enlarges slowly and usually causes no signs or symptoms other than a patch or small spot on your skin. These patches take years to develop, usually first appearing in people over 40. A small percentage of actinic keratosis lesions can eventually become skin cancer. You can reduce your risk of actinic keratoses by minimizing your sun exposure and protecting your skin from ultraviolet (UV) rays.
WHAT IS ACTINIC KERATOSIS?
If you have an actinic keratosis (AK) on your skin, you have one of the most common skin conditions that dermatologists treat. It is estimated that more than 40 million Americans develop actinic keratoses (AKs) each year. These precancerous skin growths are common because many people seldom protect their skin from the sun with sunscreen, clothing, and shade. Without sun protection, the sun’s harmful rays can damage your skin. While your body may repair some of this damage, the sun’s rays continue to damage unprotected skin. Over the years, this damage builds up and can cause precancerous changes to your skin.
WHAT CAUSES ACTINIC KERATOSIS?
AKs can result from over-exposure to sunlight upon unprotected skin. An actinic keratosis often appears as a reddish spot that develops on skin you seldom protected from the sun over the years. Tanning beds, sunlamps, or excessive exposure to the sun can also lead AKs. The amount of the harmful radiation produced by a tanning bed is similar to that of the sun, and in some cases might be stronger. AKs tend to appear on skin that has been badly damaged by the sun. AKs often appear on the face, ears, balding scalp, hands, neck, or lips. These areas tend to get the most sun.
ARTICLES FOR ACTINIC KERATOSIS
HOW CAN I TREAT ACTINIC KERATOSIS?
Photodynamic treatment is being recommended to treat pre-cancerous lesions (actinic keratosis) on your skin. These precancerous lesions can have several causes; UV radiation, genetics, exposure to such cancer-causing substances (carcinogens) as smoking (including “side smoke”), arsenic, tar or x-ray radiation. Photodynamic therapy or PDT is a treatment that uses special drugs, called photosensitizing agents, along with light to kill precancerous and cancer cells. The drugs only activate only after they have been “turned on” by exposure to certain wavelengths of light. The photosensitizing agent is applied in the office to the skin and binds to pre-cancerous or cancerous cells over 45-60 minutes. Then, light to activate this topical agent causes the drug to react with oxygen, which forms a chemical that kills the precancerous or cancerous cells.
The drug that is applied to treat precancerous cells (Actinic Keratosis) is Levulan Kerastick (aminolevulinic acid HCI) topical solution. The solution is absorbed by the actinic keratosis cells and then converted to a chemical that makes these cells extremely sensitive to certain wavelengths of light. When the actinic keratosis cells are exposed to the blue light illuminator, a reaction occurs in which the actinic keratosis cells are destroyed.
Before the photodynamic treatment, be sure to tell your healthcare provider if you are taking ANY oral medications or using topical prescriptions, or non-prescription products on the area that the provider will be treated. Bring adequate sun-protective ítems to your visit (examples: wide brimmed hats (garden hats), umbrella, sun-protective clothing) for the area that is to be treated.
You must wear a physical sunscreen if the area that is being treated will not be covered completely from any light for the next 48 hours. If you cannot find an adequate chemical-free, physical sunscreen of a high enough quality for this purpose, ACD Aesthetics does offer two options: the Elta MD UV Physical spf 41 sunscreen and the Blue Lizard spf >30 sunscreen. After the treatment is over with, we will apply one of these 2 physical suncreens and make sure you are protected from sunlight before you leave the office. Avoid exposure to sunlight or indoor ultraviolet or blue light (ex: refrigerator section for milk) for at least 40 hours after the treatment. Reapply the physical suncreen every 2 hours. We highly recommed that you stay indoors.
DOES INSURANCE COVER ACTINIC KERATOSIS TREATMENT?
We will call your insurance to see if it is covered. It is highly recommended that you call as well. The diagnosis code is L57.0 (Actinic Keratosis) and procedure codes are 96567 and J7308 . When calling insurance, make sure to document the name of the person that you spoke with. Ask if the procedure is covered, if it will be applied to a deductible, and if you have a co-pay. We should obtain your email address and make sure that you are set up on our patient portal system before you leave the office. Once we hear back from your insurance, we will message you on the patient portal system with the coverage benefits that we found out from your insurance. At this time we will also request that you message us back letting us know if you would like to proceed with the treatment and when you would like to schedule. If you opt not to use the patient portal system, we can call you but we apologize in advance if we “play phone tag”.
If you have any further questions, please ask your healthcare provider, message us on the Patient Portal, or call our office at 817-795-7546.
SCHEDULE AN APPOINTMENT TODAY
ADDRESS
711 E Lamar Blvd # 200
Arlington, TX 76011
moreinfo@acderm.com
PHONE
817-795-SKIN (7546)
HOURS
Mon – Thur | 7:00 AM – 4:00 PM
Fri | 07:00 AM – 12:00 PM
Closed on Weekends







